ABSTRACT
This study explores the key factors influencing the decision of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Binh Duong province to outsource accounting services. Using quantitative methods, including exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and multiple regression analysis on data collected from 151 SMEs, the research identifies five significant determinants: perceived benefits, service fees, service reliability, accounting expertise, and referrals. The findings provide valuable insights for both SMEs and accounting service providers in enhancing the effectiveness of outsourcing decisions and improving service quality.
Keywords: outsourcing, accounting services, SMEs, Binh Duong, decision-making.
1. Introduction
In today's increasingly complex and competitive business environment, many companies-particularly SMEs-face difficulties in managing operations, complying with regulations, and maintaining cost-effective accounting systems (Kamyabi & Devi, 2011). Limited resources, lack of expertise, and high personnel turnover further hinder their ability to meet financial reporting and tax obligations.
Outsourcing accounting services has become a practical solution, offering benefits such as cost savings, legal compliance, improved accuracy, and access to professional expertise. For newly established firms, outsourcing helps navigate initial accounting procedures and tax compliance (Vuong & Nguyen, 2019), while long-established businesses reduce costs related to staffing and mitigate operational disruptions (Tran et al., 2019).
In Binh Duong province - an economically dynamic region with many industrial zones and SMEs - the demand for professional accounting services is rising. However, the decision to outsource depends on various factors including perceived benefits, service quality, referrals, and pricing.
This study aims to identify the key factors influencing SMEs’ decisions to outsource accounting services in Binh Duong. The findings will offer insights for service providers and policymakers to improve service delivery and support businesses in making informed, cost-effective outsourcing decisions.
2. Theoretical background and hypotheses
Outsourced accounting refers to the delegation of accounting tasks to independent firms or professionals instead of maintaining an internal department. This practice offers advantages such as cost savings, access to expertise, regulatory compliance, and a focus on core business operations-particularly beneficial for SMEs and startups. However, it also requires careful provider selection and oversight to ensure service quality and timeliness (Journal of Accounting and Auditing, 2020).
The decision to outsource accounting services can be understood through several theoretical lenses:
- Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) explains that behavioral intention is driven by individual attitudes and perceived social norms.
- Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) (Ajzen, 1991) extends TRA by adding perceived behavioral control, offering a more comprehensive model of intentional behavior.
- Consumer Behavior Theory (Kotler, 2013) describes the decision-making process through stages such as need recognition, information search, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase behavior-many of which are relevant in outsourcing service selection.
- Resource-Based Theory (RBT) (Barney, 1991; McIvor, 2009) posits that firms should focus on core competencies while outsourcing non-core functions to external providers with greater capabilities. This strategy supports competitive advantage through resource optimization.
Based on these theories and prior empirical findings, the study proposes the following hypotheses:
H1: Benefits have a positive impact on the decision to outsource accounting services for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
H2: Service fees have a positive impact on the decision to outsource accounting services for SMEs.
H3: Reliability has a positive impact on the decision to outsource accounting services for SMEs.
H4: Accounting professional level has a positive impact on the decision to outsource accounting services for SMEs.
H5: Referrals have a positive impact on the decision to outsource accounting services for SMEs.
Based on the research results of previous authors, this article proposes the research model as follows.
![]()
Figure 1. Proposed Research Model, 2025
3. Research methodology
This study employed a quantitative, cross-sectional design using a structured questionnaire to examine factors influencing SMEs’ decisions to outsource accounting services in Binh Duong province.
3.1. Data collection
Following the guideline of Hair et al. (2006), a sample size of at least 140 observations was required to perform exploratory factor analysis (EFA), given the 28 measurement items used. The questionnaire was distributed to 200 SMEs using non-probability convenience sampling. After screening for completeness and accuracy, 151 valid responses were retained for analysis.
The questionnaire focused on five independent variables: Benefits (BFT), Service Fees (SF), Reliability (RBL), Accounting Professional Level (APL), and Referrals (REF). To ensure clarity and content validity, a pilot test was conducted with a small group of SMEs before final distribution. Data were collected through both email and in-person delivery.
3.2. Data analysis
Collected data were analyzed using SPSS software through the following steps:
- Descriptive statistics provided an overview of respondent demographics and business characteristics.
- Cronbach’s Alpha tested the reliability of measurement scales, ensuring internal consistency of the observed items.
- Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) was used to identify underlying constructs and reduce dimensionality.
- Multiple linear regression assessed the impact of five independent variables (Benefits, Service Fees, Reliability, Accounting Expertise, and Referrals) on the outsourcing decision.
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Descriptive statistics
Among the 151 respondents, 53.6% were male and 46.4% female. In terms of positions, 48.7% were chief accountants, 27.2% were deputy directors, and 25.2% were directors. Most enterprises were limited liability companies (84.8%) and had annual revenues under VND 50 billion.
4.2. Reliability analysis
Cronbach’s Alpha coefficients were used to evaluate the internal consistency of the measurement scales. All constructs exceeded the minimum threshold of 0.6, indicating acceptable reliability. Specifically, “Reliability” had the highest Alpha (0.838), followed by “Decision to Outsource” (0.830), “Perceived Benefits” (0.827), “Referral Sources” (0.795), “Service Fees” (0.791), and “Accounting Expertise” (0.791).
Corrected Item-Total Correlation values were all above 0.3, and no items required elimination. These results confirm that the scales were reliable and suitable for subsequent exploratory factor analysis.
4.3. Exploratory factor analysis
EFA was performed using Principal Component Analysis with Varimax rotation. The KMO value was 0.864 and Bartlett’s Test was significant (p < 0.001), confirming the dataset’s suitability for factor analysis.
Five factors with eigenvalues >1 were extracted, explaining 61.89% of total variance-exceeding the recommended 50% threshold. All 22 items had factor loadings above 0.5, and no items were removed. The results indicate strong construct validity and confirm the theoretical structure of the measurement model.
4.4. Multiple regression analysis
The multiple regression model explains 69% of the variance in the decision to outsource accounting services (R² = 0.690), indicating a high explanatory power. The Durbin-Watson statistic is 2.019, confirming that the residuals are not autocorrelated and that the model meets key assumptions.
As shown in Table 1, all five independent variables - Benefits (BFT), Service Fees (SF), Reliability (RBL), Accounting Professional Level (APL), and Referrals (REF) - have statistically significant and positive effects on outsourcing decisions (p < 0.001). Among these, Benefits (β = 0.296) and Referrals (β = 0.277) show the strongest standardized coefficients, indicating they are the most influential predictors.
Variance Inflation Factors (VIFs) for all variables range from 1.311 to 1.366, well below the commonly accepted threshold of 10, suggesting that multicollinearity is not a concern. These findings confirm the reliability and robustness of the regression model.
Table 1. The results of Multiple Regression Analysis
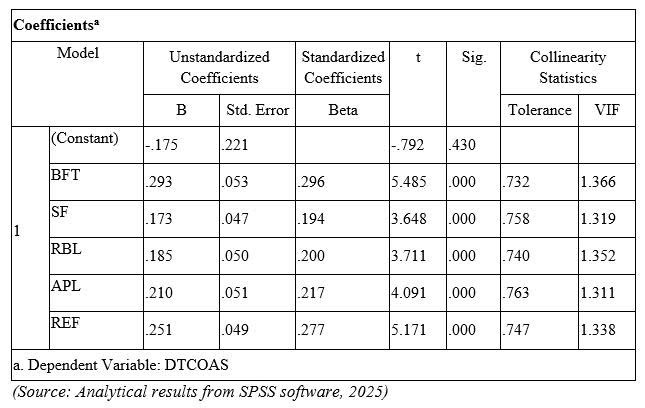
4.5. Discussion
The analysis reveals that all five factors significantly influence SMEs’ decisions to outsource accounting services.
Benefits (β = 0.296) had the strongest impact, indicating that firms value the perceived advantages of outsourcing, such as improved efficiency, regulatory compliance, and reduced accounting risks. This confirms that SMEs are motivated by practical outcomes when choosing external services.
Referrals (β = 0.277) also played a critical role, highlighting the importance of social influence. Recommendations from trusted sources like tax officers, partners, or peers help reduce uncertainty and encourage outsourcing decisions.
Accounting Expertise (β = 0.217) shows that the perceived competence of service providers fosters trust and confidence in outsourcing arrangements. SMEs are more likely to outsource when they believe providers possess the necessary knowledge and skills.
Reliability (β = 0.200) suggests that service dependability is an essential consideration. Consistent and trustworthy service delivery enhances operational stability and reduces risk for SMEs.
Finally, Service Fees (β = 0.194) indicate that cost remains a relevant factor, though not the most dominant. Affordable pricing allows SMEs to access professional accounting support without incurring the high costs of maintaining an in-house team.
These findings confirm that outsourcing decisions are influenced by both tangible benefits and relational factors, with an emphasis on trust, expertise, and outcome effectiveness.
5. Conclusion and recommendations
5.1. Conclusion
This study identified five key factors influencing the decision of SMEs in Binh Duong province to outsource accounting services: perceived benefits, service fees, referrals, reliability, and accounting expertise. All factors showed statistically significant and positive impacts, with perceived benefits and referrals being the most influential. These results underscore the importance of both practical value and social influence in shaping outsourcing behavior among SMEs.
5.2. Recommendations
To enhance service adoption, accounting service providers should:
- Ensure compliance and reliability by minimizing errors, maintaining accurate records, and delivering timely reports.
- Improve service quality and customer care to foster trust and encourage positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Strengthen professional competence by employing qualified staff and offering advisory support.
- Offer flexible pricing packages that address varying business needs and increase market competitiveness.
Implementing these recommendations will support service providers in meeting client expectations and encouraging long-term cooperation with SMEs.
References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179-211.
Barney, J. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management, 17(1), 99-120.
Everaert, P., Sarens, G., & Rommel, J. (2010). Using transaction cost economics to explain outsourcing of accounting. Small Business Economics, 35(1), 93-112.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, Attitude, Intention and Behavior: An Introduction to Theory and Research. Addison-Wesley.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate Data Analysis (7th ed.). Pearson.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2013). Marketing Management (14th ed.). Prentice Hall.
McIvor, R. (2009). How the resource-based and the transaction cost frameworks complement each other in outsourcing. Journal of Operations Management, 27(1), 45-63.
Ngo, T. H. (2022). Determinants of accounting service outsourcing among SMEs in Ho Chi Minh City. Journal of Industry and Trade, 12, 45-51.
Vuong, Y. L., & Nguyen, H. D. (2019). Factors influencing the outsourcing of accounting services by SMEs. Journal of Tay Do University, 7, 132-147.
Author’s biography
Truong Van Sang
Tay Do University
Các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến quyết định thuê ngoài dịch vụ kế toán của doanh nghiệp nhỏ và vừa: Nghiên cứu tại tỉnh Bình Dương
Trương Văn Sang
Trường Đại học Tây Đô
Tóm tắt:
Nghiên cứu này phân tích các yếu tố chính ảnh hưởng đến quyết định thuê ngoài dịch vụ kế toán của các doanh nghiệp nhỏ và vừa (SME) tại tỉnh Bình Dương. Sử dụng phương pháp định lượng, bao gồm phân tích nhân tố khám phá (EFA) và hồi quy đa biến trên dữ liệu thu thập từ 151 doanh nghiệp, nghiên cứu xác định có năm yếu tố có ảnh hưởng đáng kể, gồm: lợi ích cảm nhận, chi phí dịch vụ, độ tin cậy của dịch vụ, năng lực chuyên môn kế toán và yếu tố giới thiệu. Kết quả nghiên cứu cung cấp những gợi ý hữu ích cho cả doanh nghiệp và các nhà cung cấp dịch vụ kế toán trong việc nâng cao hiệu quả quyết định thuê ngoài và cải thiện chất lượng dịch vụ.
Từ khoá: thuê ngoài, dịch vụ kế toán, doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ, Bình Dương, ra quyết định
[Tạp chí Công Thương - Các kết quả nghiên cứu khoa học và ứng dụng công nghệ, số 26 năm 2025]
