Abstract
This study investigates the factors influencing the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Can Tho City. Drawing on survey data from local SMEs, the empirical analysis reveals that six factors, including: accounting information systems, accountants’ professional competence, tax regulations, accounting data quality, management commitment, and internal control systems, exert a positive and statistically significant effect on the quality of accounting information. The findings offer practical managerial insights for enhancing accounting information quality and promoting greater financial transparency within SMEs.
Keywords: accounting information quality, financial statements, small and medium-sized enterprises, Can Tho City.
1. Introduction
In the context of economic integration, increasing requirements for financial transparency have highlighted the importance of accounting information quality in financial statements for stakeholders’ decision-making. High-quality accounting information helps reduce information asymmetry, enhance the reliability of financial statements, and improve the efficiency of resource allocation in the economy (Akerlof, 1970; IASB, 2018).
In Vietnam, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) account for more than 97% of operating enterprises and play a vital role in economic growth and employment creation. However, recent empirical studies indicate that the quality of accounting information in enterprises’ financial statements remains limited, mainly due to weaknesses in accounting organization, professional competence of accounting staff, internal control systems, and regulatory compliance. Evidence from listed enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City shows that deficiencies in accounting practices significantly reduce the reliability of financial statement information (Le Hoang Van Trang et al., 2020), while studies by Nguyen Dinh Chien and Tran Thi Giang (2023) and Ngo Ngoc Nguyen Thao (2023) further confirm the influence of internal organizational factors and regulatory pressures on accounting information quality.
From the perspectives of signaling theory and agency theory, transparent and reliable financial reporting enables enterprises to convey credible information to stakeholders, improve access to external financing, and reduce agency costs through enhanced monitoring mechanisms (Spence, 1973; Jensen & Meckling, 1976).
Can Tho City, the economic center of the Mekong Delta, has a large concentration of SMEs, yet empirical evidence on accounting information quality at the local level remains limited. Therefore, this study aims to identify the factors affecting the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs in Can Tho City, thereby providing a basis for appropriate managerial implications.
2. Theoretical framework and research hypotheses
2.1. Theoretical background
The quality of accounting information in financial statements refers to the extent to which information meets the decision-making needs of users. According to IASB (2018), financial information is considered high quality when it is relevant and faithfully represented, and when it possesses enhancing qualitative characteristics such as comparability, verifiability, timeliness, and understandability. Numerous studies confirm that accounting information quality determines the reliability of financial statements and directly affects the effectiveness of economic decision-making (DeLone & McLean, 2003; Xu, 2003), especially for SMEs, which often face limitations in resources and governance systems.
This study is grounded in three fundamental theories: information asymmetry theory, signaling theory, and agency theory. Information asymmetry theory suggests that disparities in information between managers and stakeholders may lead to adverse selection and moral hazard (Akerlof, 1970). Signaling theory posits that financial statements serve as a mechanism through which enterprises signal their financial position and prospects; high-quality reporting sends positive signals and enhances access to capital (Spence, 1973). Agency theory emphasizes the role of financial statements in monitoring managerial behavior and reducing agency costs by improving information transparency (Jensen & Meckling, 1976).
From these theoretical perspectives, enhancing the quality of accounting information in financial statements is essential to reducing information asymmetry, strengthening stakeholder trust, and improving corporate governance, particularly in SMEs.
2.2. Research hypotheses
Based on the theoretical foundations and prior empirical studies, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H1: Accounting information systems have a positive impact on the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs.
H2: Accountants’ professional competence has a positive impact on the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs.
H3: Tax regulations have a positive impact on the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs.
H4: Accounting data quality has a positive impact on the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs.
H5: Management commitment has a positive impact on the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs.
H6: Internal control systems have a positive impact on the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs.
Based on the theoretical framework and prior empirical studies, this study proposes a research model illustrating the relationships between the influencing factors and the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs in Can Tho City, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Proposed research model
![]()
(Source: Compiled by the author, 2025)
3. Research methodology
3.1. Data collection
According to Hair et al. (2006), with 25 observed variables, the minimum sample size required for exploratory factor analysis (EFA) is 125 observations. This study surveyed 200 SMEs using a convenience sampling method. After excluding invalid responses, 150 valid questionnaires were retained for analysis.
The respondents included managers and accounting staff working in SMEs. All questionnaire items were measured using a five-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (“strongly disagree”) to 5 (“strongly agree”). Data were collected through both direct and online surveys.
3.2. Data analysis
Data were processed using SPSS software. Cronbach’s Alpha was employed to test the reliability of measurement scales; exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was conducted to identify factor structures; and multiple linear regression analysis was applied to assess the impact of the proposed factors on accounting information quality in SMEs’ financial statements.
4. Research results and discussion
4.1. Descriptive statistics
The study analyzed 150 valid questionnaires collected from SMEs in Can Tho City. The sample structure is consistent with the characteristics of accounting human resources in this type of enterprise.
The results indicate that female respondents account for 54.7%, higher than males (45.3%). Regarding educational level, respondents with college and university degrees represent 57.3%, while those with postgraduate degrees account for 42.7%, reflecting a relatively solid professional background among accounting personnel. Most respondents have 5-10 years of work experience (56.6%) and hold accounting staff positions (72.7%), with participation from managerial staff, ensuring diverse perspectives.
4.2. Reliability analysis
The Cronbach’s Alpha results show that all measurement scales meet reliability requirements, with coefficients ranging from 0.618 to 0.810. All observed variables have item total correlation coefficients greater than 0.3, and no variables were eliminated, confirming that the scales are reliable and suitable for further analysis.
4.3. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA)
EFA results for the independent variables indicate a KMO value of 0.677 and a statistically significant Bartlett’s test (Sig. = 0.000). Six factors were extracted, explaining 65.275% of the total variance, consistent with the proposed research model. All factor loadings exceed 0.5, with no problematic items.
For the dependent variable, EFA extracted a single factor explaining 51.250% of the variance, indicating that the accounting information quality scale is structurally appropriate.
4.4. Regression results and hypothesis testing
Multiple linear regression analysis confirms that the research model fits the survey data well. The adjusted R² value is 0.534, indicating that the independent variables explain 53.4% of the variation in accounting information quality. The F-test is statistically significant (Sig. = 0.000). The Durbin-Watson statistic equals 1.87, which lies within the acceptable range of 1.5 to 2.5, indicating that the regression model does not suffer from autocorrelation.
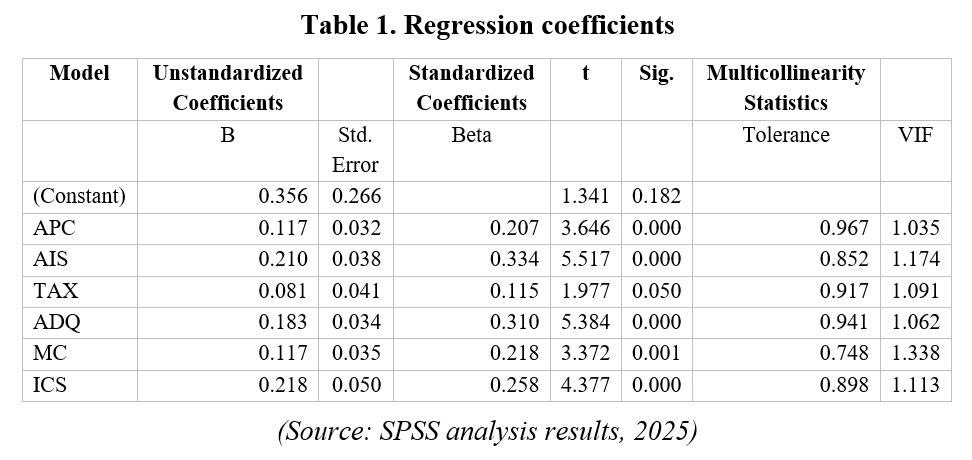
The estimation results reveal that all six factors have positive and statistically significant effects on accounting information quality. Among them, accounting information systems exert the strongest influence, followed by accounting data quality, internal control systems, management commitment, accountants’ competence, and tax regulations. Diagnostic tests indicate that the regression model satisfies the necessary assumptions.
These findings highlight the critical role of system-related factors, particularly accounting information systems, consistent with the studies of Xu (2003) and DeLone & McLean (2003). Human, managerial, and regulatory factors also significantly affect accounting information quality in SMEs in Can Tho City.
5. Conclusions and managerial implications
5.1. Conclusions
This study aims to identify the factors affecting the quality of accounting information in the financial statements of SMEs in Can Tho City. The results indicate that six factors accounting information systems, accounting data quality, internal control systems, management commitment, accountants’ competence, and tax regulations have positive and statistically significant impacts on accounting information quality.
System-related and internal governance factors exert stronger effects than legal factors. The findings provide additional empirical evidence supporting information asymmetry theory and agency theory in the context of Vietnamese SMEs.
5.2. Managerial implications
Based on the findings, SMEs should prioritize improving accounting information systems in line with their scale and operational characteristics to enhance the accuracy, timeliness, and consistency of accounting information. The adoption of appropriate accounting software, combined with standardized information processing procedures, can significantly improve financial reporting quality.
Enterprises should also focus on improving the quality of accounting input data through strict control of accounting documents to ensure that data are recorded fully, validly, and in accordance with the substance of economic transactions. Strengthening internal control systems will help reduce errors and fraud, thereby enhancing the reliability of accounting information.
In addition, management commitment to financial transparency plays a critical guiding role in maintaining accounting information quality. Managers should create favorable conditions for accounting departments to perform their professional functions while investing in training and continuous professional development for accounting staff. Compliance with tax regulations also supports transparency and reliability in SMEs’ financial reporting.
References
Akerlof, G. A. (1970). The market for “lemons”: Quality uncertainty and the market mechanism. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 84(3), 488-500.
DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9-30.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2006). Multivariate data analysis (6th ed.). Pearson Education.
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). (2018). Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting. IFRS Foundation.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(4), 305-360.
Lê, H. V. Trang, Võ, V. Hiền, & Nguyễn, H. Thơ. (2020). Các nhân tố ảnh hưởng đến chất lượng thông tin kế toán trên báo cáo tài chính của các doanh nghiệp niêm yết tại Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh. Tạp chí Khoa học Đại học Mở Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh, 15(3), 143-158.
Ngo Ngoc Nguyen Thao. (2023). Factors affecting the quality of accounting information in financial statements of enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City. Industry and Trade Magazine.
Nguyen, Dinh Chien, & Tran, Thi Giang. (2023). Factors affecting the quality of accounting information on financial statements of small and medium-sized enterprises in Hue. Finance Journal, (5), 150-154.
Spence, M. (1973). Job market signaling. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 87(3), 355-374.
Xu, H. (2003). Critical success factors for accounting information systems data quality. Journal of Information Science, 29(6), 507-521.
Các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến chất lượng thông tin kế toán trong báo cáo tài chính của các doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ (SMEs) tại TP.Cần Thơ
Thái Thị Bích Trân
Trường Đại học Tây Đô
Tóm tắt:
Nghiên cứu này khảo sát các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến chất lượng thông tin kế toán trong báo cáo tài chính của các doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ (SMEs) tại TP.Cần Thơ. Dựa trên dữ liệu khảo sát từ các SMEs địa phương, phân tích thực nghiệm cho thấy sáu yếu tố, gồm: hệ thống thông tin kế toán, năng lực chuyên môn của kế toán viên, quy định thuế, chất lượng dữ liệu kế toán, cam kết của ban lãnh đạo, và hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ, có tác động tích cực và có ý nghĩa thống kê đến chất lượng thông tin kế toán. Các kết quả nghiên cứu cung cấp những gợi ý quản lý thực tiễn nhằm nâng cao chất lượng thông tin kế toán và thúc đẩy tính minh bạch tài chính trong các SMEs.
Từ khoá: chất lượng thông tin kế toán, báo cáo tài chính, doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ, TP.Cần Thơ.
[Tạp chí Công Thương - Các kết quả nghiên cứu khoa học và ứng dụng công nghệ, số 01 năm 2026]

